
Introduction
In terms of web security, SSL certificates are the unsung heroes. They make sure your data is encrypted and out of the hands of spies. However, what takes place in the event of a glitch in the procedure, such as the infamous “unable to get local issuer certificate” error? Let’s examine this prevalent problem and its potential solutions.
Understanding SSL Certificates
What is an SSL Certificate?
A digital certificate known as an SSL (Secure Socket Layer) certificate verifies the legitimacy of a website and permits an encrypted connection. Consider it a website’s digital passport, confirming the security of the data being delivered.
Types of SSL Certificates
There are several types of SSL certificates, including:
- Domain Validated (DV) Certificates: Basic encryption, usually for personal websites.
- Organization Validated (OV) Certificates: Higher validation, typically for business websites.
- Extended Validation (EV) Certificates: The highest level of validation, showing a green address bar in browsers.
How SSL Certificates Work
A public key and a private key are the two keys that SSL certificates employ to encrypt data. By encrypting the data being communicated, the SSL certificate guarantees a safe connection when a browser connects to a website.
Common SSL Certificate Issues
Overview of SSL Certificate Problems
SSL certificates may have a number of issues, such as mismatched domain names or expired certificates. The error “unable to get local issuer certificate” is one that frequently irritates users.
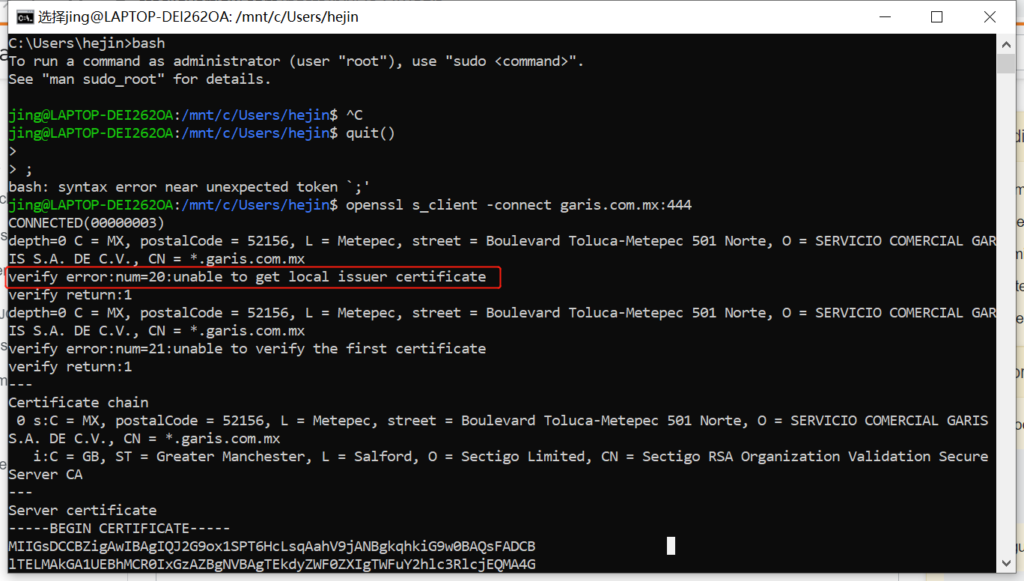
Specific Focus: Unable to Get Local Issuer Certificate
This issue usually arises when the system cannot locate the intermediate certificate required to establish confidence because the certificate chain is incomplete.
The “Unable to Get Local Issuer Certificate” Error
Explanation of the Error
The problem “unable to get local issuer certificate” means that the trusted root certificate authority (CA) is not present on your computer, which prevents it from validating the SSL certificate.
Common Causes of the Error
Several factors can cause this error:
- Outdated CA certificates on the server or client
- Incorrect certificate installation
- Missing intermediate certificates
Impact of the Error on Websites
This mistake can keep visitors from visiting your website, which would decrease traffic and trust. Users may be discouraged from continuing by warning messages that appear in their browsers.
Diagnosing the Error
Steps to Identify the Problem
- Check the Browser Console: Look for SSL errors.
- Use SSL Tools: Tools like SSL Labs can help diagnose issues.
- Review Server Logs: Check for any SSL-related errors in your server logs.
Tools for Diagnosing SSL Certificate Issues
- SSL Labs: Provides a detailed analysis of your SSL configuration.
- OpenSSL: A command-line tool to test and verify certificates.
- Browser Developer Tools: Inspect SSL errors directly in your browser.
Fixing the “Unable to Get Local Issuer Certificate” Error
Updating CA Certificates
Make sure your CA certifications are current. The package manager on your operating system or reliable websites like Mozilla are good places to get the most recent CA certificates.
Verifying the Certificate Chain
Verify that each intermediary certificate has been installed and linked properly. By doing this, you can be sure that the browser can validate the SSL certificate and that the certificate chain is complete.
Correcting Server Configuration
Verify that the SSL certificate chain is being correctly served by your server by checking its setup. The configuration files on your server might need to be updated for this.
Preventing SSL Certificate Errors
Regular Updates and Maintenance
Make sure your CA and SSL certifications are up to current. Check for updates frequently, and make sure to renew your certificates before they expire.
Proper Certificate Installation
Make sure your SSL certificates are installed correctly. Observe the recommendations and best practices that your certificate authority has issued.
Importance of Trusted Certificate Authorities
Obtain your SSL certificates from reliable and trustworthy certificate authority at all times. This guarantees that all of the major browsers will recognize your certificates.
SSL Certificates and Different Operating Systems
Windows
CA certificate upgrades are frequently required manually on Windows computers. To maintain and update your certificates, use the Windows Certificate Manager.
macOS
Although SSL certificates are often handled automatically by macOS, you can manage and update certificates using the Keychain Access application.
Linux
Linux users can manage SSL certificates using tools like OpenSSL and update CA certificates using package managers like apt or yum.
Impact on Browsers and Users

How Different Browsers Handle SSL Errors
SSL failures may be handled differently by different browsers. Some may display a warning and permit users to continue, while others may entirely restrict access.
User Experience and Trust Issues
User trust can be severely impacted by SSL problems. When users see these issues, they could think your website is dangerous and leave, which could hurt your brand.
Best Practices for SSL Certificate Management
Regular Audits
Conduct regular audits of your SSL certificates to ensure they are valid and properly installed.
Automated Monitoring Tools
Use automated tools to monitor your SSL certificates and alert you to any issues or impending expirations.
Keeping Abreast with Latest Security Practices
Stay updated with the latest security practices and ensure your SSL configuration meets current standards.
SSL Certificates in the Modern Web Landscape
The Role of SSL in SEO
SSL certificates play a crucial role in SEO. Google prioritizes secure websites, so having a valid SSL certificate can boost your search engine rankings.
SSL Certificates and GDPR Compliance
For websites handling personal data, SSL certificates are essential for GDPR compliance. They ensure that data is encrypted and secure.
Future Trends in SSL Technology
The future of SSL technology includes advancements like quantum-resistant encryption and more automated certificate management solutions.
Conclusion
Managing SSL certificates can seem daunting, but it’s crucial for maintaining a secure and trustworthy website. Regular updates, proper installation, and staying informed about the latest security practices can help prevent issues like the “unable to get local issuer certificate” error.
FAQs
What is an SSL Certificate?
An SSL certificate is a digital certificate that authenticates a website’s identity and enables encrypted connections, ensuring data security.
How Do I Know if My SSL Certificate is Working Properly?
You can check your SSL certificate’s status using online tools like SSL Labs or browser developer tools to ensure it’s correctly installed and trusted.
What Happens if My SSL Certificate Expires?
If your SSL certificate expires, your website will display security warnings, and users may not be able to access it, leading to a loss of traffic and trust.
Can I Use a Self-Signed SSL Certificate?
While you can use a self-signed SSL certificate, it’s not recommended for public websites as browsers won’t trust it, leading to security warnings for users.
How Often Should I Renew My SSL Certificate?
Typically, SSL certificates need to be renewed annually, though some providers offer longer terms. It’s crucial to renew them before they expire to maintain security.





